What Does a Fast Heartbeat Mean in a Baby
By: Orhan Kilinc, Medico, FAAP, and Christopher Southward. Snyder, Doc, FAAP
The eye is 1 of the almost agile muscles in the body, beating some fifty million times in a child'south get-go yr of life. It'southward normal for a kid'south heartbeat to speed up or slows down equally they play, sleep and grow.
Only what if your child's heartbeat seems faster or slower than it should be, or has an unusual design? In this article, the American Academy of Pediatrics describes normal heart rate fluctuations in kids, and what might be cause for business organisation.
Reasons for irregular heartbeats
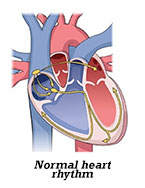 Unremarkably, special "pacemaker" cells in the heart send electrical impulses from upper to lower chambers (atria and ventricles), which take turns squeezing and relaxing to pump claret throughout the body. There are many factors that can influence this rhythm. These include physical activity, stress or excitement, for instance. Fever, dehydration, and medical conditions like anemia can besides play a role. So tin can certain medications or consuming energy drinks and other caffeine-containing beverages. In improver, some children are built-in with congenital conditions that affect the heart's muscles or electrical pathways and the fashion it pumps.
Unremarkably, special "pacemaker" cells in the heart send electrical impulses from upper to lower chambers (atria and ventricles), which take turns squeezing and relaxing to pump claret throughout the body. There are many factors that can influence this rhythm. These include physical activity, stress or excitement, for instance. Fever, dehydration, and medical conditions like anemia can besides play a role. So tin can certain medications or consuming energy drinks and other caffeine-containing beverages. In improver, some children are built-in with congenital conditions that affect the heart's muscles or electrical pathways and the fashion it pumps.
Irregular heartbeats that are usually normal
Irregular heartbeats, besides chosen arrhythmias, are a common reason for referral to a pediatric cardiologist. Almost often, these irregularities plough out to exist perfectly normal. Examples of these common simply ordinarily harmless arrhythmias include:
Respiratory sinus arrhythmia - the almost mutual irregular heart rate in children. It's acquired by the normal change in how fast blood returns to the heart when they breath in or out. The middle beats faster when they inhale, and slower when they exhale. The name "arrhythmia" is really misleading, since this variation in heartbeats occurs in all healthy children in varying degrees.
Premature or "skipped" heart beats - seen in upwardly to 75% of pediatric patients. These irregular beats may start in either the superlative chambers (premature atrial contractions) or the bottom chambers (premature ventricular contractions) of the heart. Patients feel like their heart "skipped" a crush due to a interruption in the rhythm followed past a more than forceful beat.
Normal Heart Rate Range for Children & TeensVariations in a child's heart rate is normal. Generally, though, a child's eye rates slows equally they become older. For example, a centre rate of 130 to 150 beats per infinitesimal is normal for a newborn baby, only it would be considered fast for a school age child. An able-bodied teenager may have a middle rate of fifty at rest but could have eye charge per unit of 180 during heavy exercise. To check your child's pulse or eye rate, gently feel for a slight shell inside the wrist, the cheat of the elbow, or side of neck. Count beats for 15 seconds, and then multiply by four.
|
|---|
Irregular heart rhythms that may need evaluation & treatment
There are other types of irregular heartbeats that may need be treated or monitored. These include:
Abnormally fast heartbeats
Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is the most common abnormal pediatric heart rhythm, affecting as many every bit 1 in 250 children. It happens when electric signals in the upper chambers of the centre misfire and cause a sudden burst of abnormally fast, "racing" heartbeats that last for seconds, minutes or longer. About half of children with SVT, sometimes called atrial tachycardia, are diagnosed every bit infants. Episodes of SVT normally go away by a child'due south first birthday, although it can return.
At that place are different types and causes of SVT, including:
- Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome affects children built-in with an extra electrical pathway in the center. That extra pathway may allow impulses to movement in a unlike management and faster than usual.
- Atrial flutter & atrial fibrillation happens when electrical signals from the upper bedchamber of the heart are faster than those in the lower chamber, causing the centre to flutter rather than fully squeezing for a regular beat. Atrial fibrillation is some other blazon of abnormally fast, quivering heart rhythm that is similar to atrial flutter, merely the abnormally fast beats are less regular. These conditions make information technology hard for the heart to pump blood effectively and increases the gamble of problems like claret clots. Both are much less mutual than other types of SVT. Research suggests they may exist inherited genetically or linked to congenital heart abnormalities or eye muscle disorders like cardiomyopathy.
Ventricular tachycardia (VT) is a series of heartbeats starting in the lower chambers of the middle, rather than the upper chambers like normal, that cause an abnormally fast rhythm. It is rare in children, but early on identification can be lifesaving since it tin raise the take chances of sudden cardiac abort. One type of VT is Long QT syndrome, an inherited condition that affects an estimated 1 in 2,500 people. Information technology causes the lower chambers of the heart to take too long to contract and release, causing a fast and chaotic heart rhythm.
Abnormally slow heartbeat
Bradycardia – when the heart rate is beneath the normal low range for a kid'due south age. In children, two of the most common types are:
- Sinus bradycardia is seen more often in premature infants. Possible causes include medications the babe was exposed to earlier birth, breathing problems or a drop in body temperature called hypothermia.
- Eye cake is when electrical signals are prevented from passing from the upper to lower chambers of the heart. The condition oft is caused by structural problems in the heart that bear upon the atrioventricular (AV) node, a cluster of specialized heart cells in the right atrium that act as a natural "pacemaker."
Signs & symptoms of an abnormal eye rhythm in children
Infants with abnormal heart rhythms may seem extra irritable or fussy, accept feeding difficulties, appear pale, and lack energy. Older children tend to have more than specific symptoms such as feeling a fluttering or pounding known every bit centre palpitations, lightheadedness or fainting, chest pain or discomfort, and difficulty breathing.
How are abnormal heart rhythms diagnosed?
If your child's doctor suspects a heart rhythm problem after the concrete exam, he or she will recommend cardiac testing, which may include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). This fast and elementary test usually is the get-go i recommended to check for aberrant rhythm. It is usually able to ostend a diagnosis, but sometimes additional testing may be needed.
- Wearable heart monitors. If a heart rhythm problem seems to come up and go, or happens merely in certain settings, a wearable heart monitor may help with diagnosis. Devices such every bit a Holter monitor let an older child printing button when they experience symptoms over the course of a twenty-four hour period or more than. The doctor tin then wait at what the monitor showed was happening in the eye at that moment.
- Stress examination. If the abnormal eye rhythm tends to happen generally during practise, the doctor may order an do stress test. Your kid rides a stationary wheel or runs on a treadmill while the doctor monitors the heart rhythm.
- Tilt-table test. For children with abnormal rhythms linked to fainting, a tilt examination can prove how centre charge per unit and blood pressure changes when a child goes from lying downwards to continuing up.
- Imaging tests. Although uncommon, sure heart rhythm conditions may signal bug with the heart's construction. In these cases, imaging tests such as an echocardiogram (ultrasound of the middle) may be needed.
Your pediatrician will likely refer you to a pediatric cardiologist for follow up. A pediatric electrophysiologist, who specializes in testing for centre rhythm disorders, may also be part of your kid's care team.
Handling for arrythmia
Although heart rhythm disorders can be worrisome, treatments and cures are available. Many heart rhythm problems can be controlled with medications. Implantable devices such as artificial pacemakers can also help keep heart rhythms regular. Other options include corrective surgery and other procedures such as radiofrequency ablation, which uses radio waves to heat up certain heart cells in the heart to prevent them from letting electrical currents through.
Additional Information :
- Dizziness and Fainting in Teens
- Higher with Built Heart Disease
Virtually Dr. Kilinc:
 Orhan Kilinc , Md, FAAP, a pediatric electrophysiologist at Joe DiMaggio Children'due south Hospital, is a member of the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) Section on Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery, is, and the AAP Florida Chapter.
Orhan Kilinc , Md, FAAP, a pediatric electrophysiologist at Joe DiMaggio Children'due south Hospital, is a member of the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) Section on Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery, is, and the AAP Florida Chapter.
About Dr. Snyder:

Christopher South. Snyder, MD, FAAP , Chair of the AAP Department on Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery, is Manager of Pediatric Cardiology at Rainbow Babies and Children's Hospital, Example Western Reserve Academy School of Medicine. He is too a member of the Ohio AAP chapter.
Image source: U.Southward. National Library of Medicine
The data contained on this Web site should not exist used every bit a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. In that location may exist variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
Source: https://www.healthychildren.org/English/health-issues/conditions/heart/Pages/Irregular-Heartbeat-Arrhythmia.aspx
0 Response to "What Does a Fast Heartbeat Mean in a Baby"
Publicar un comentario